Size
Suture size centers around “0” suture, decreasing in size with “2-0”, “3-0”, etc. The smallest size that provides sufficient tensile strength should be used as larger suture size is associated with tissue injury and potentially increased tissue reactivity.
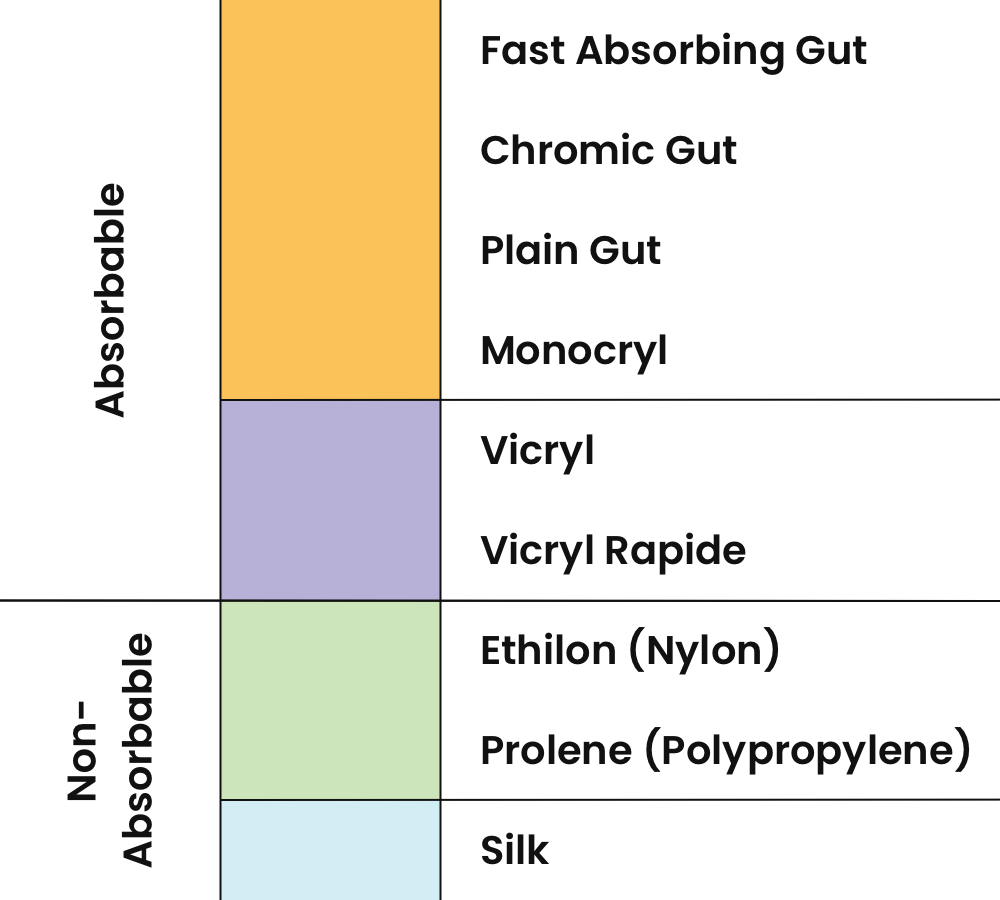
Degradation
Absorbable
Made from natural mammalian collagen (ex. gut) or synthetic materials, absorbable sutures degrade over time and do not require removal.
| Type | Effective Support |
|---|---|
| Fast Absorbing Gut | 5-7 days |
| Plain Gut | 8-9 days |
| Vicryl Rapide | 10 days |
| Chromic Gut | 10-21 days |
| Vicryl | 21 days |
Non-Absorbable
Made from natural silk or synthetic materials such as nylon or polypropylene – these require removal.
Strand Composition
Monofilament
Composed of a single strand, these have less resistance when passing through tissue and may be less prone to infection. However, their simple structure may be more prone to damage during the repair or breakage later.
Multifilament
Several strands braided together to create a suture with greater tensile strength though increased resistance passing through tissue and perhaps an increased risk of infection.
Common Suture Classification